-
Step 1: With GitHub set up and Visual Studio Code installed, you need to install and configure Git on
your local machine. Installing Git will allow you to pull (copy) the repository / code from GitHub to your
local machine. Based on the last step on the previous guide (Step By Step
— Install Visual Studio Code), you should be on the Visual Studio Code "getting started" screen.
Feel free to take a look at the different features or check out help files, articles, etc. about different
features. The details of how Visual Studio Code works is beyond the scope of this article. Note: Please
ensure you reboot your machine before proceeding if you have not rebooted it since installed Visual
Studio Code.
-
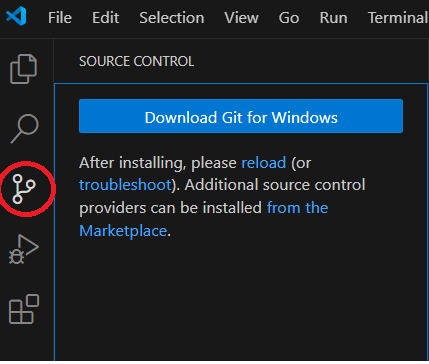
Step 2: In Visual Studio Code, if you click the "Source Control" option on the left side menu bar,
you will be taken to a screen where you will see a button which says "Download Git for Windows" (or
whichever OS you are using). Click the button to download Git.
-
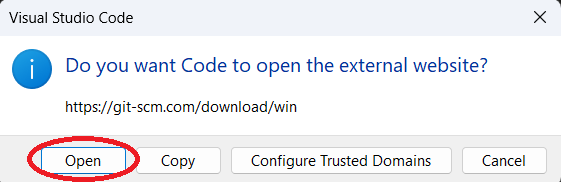
Step 3: You may be prompted to allow Visual Studio Code to open the link to the externa website.
Click "Open."
-
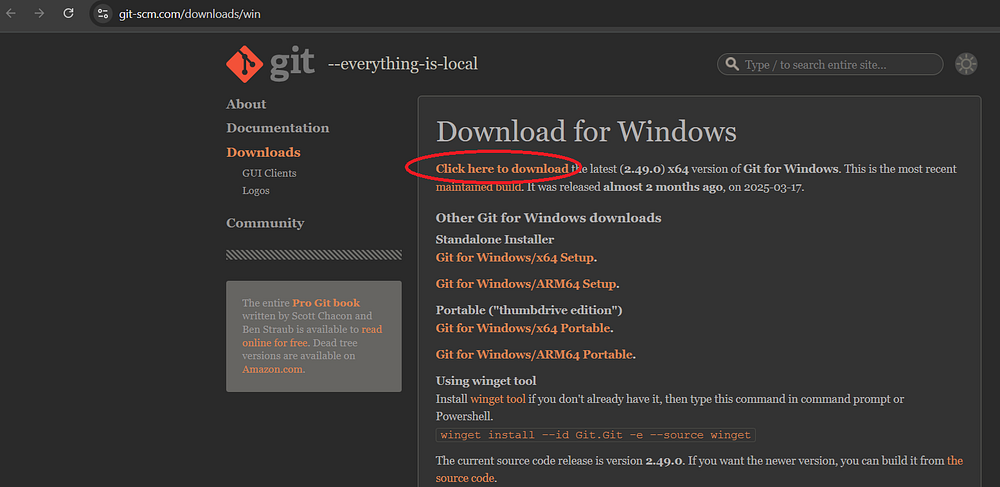
Step 4: You should be taken to the Git homepage where you should see a link to download Git. Click
the link and download Git, or choose a different link if you want a different version. The author used the
default link.
-
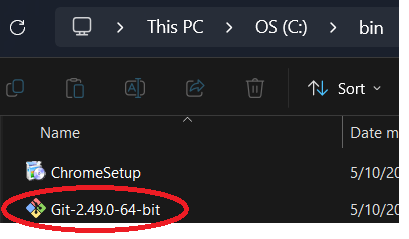
Step 5: Once the file is downloaded, you may want to put it into another location before installing.
The author uses a "bin" folder he created for this purpose. Once the file is where you want it, double click
it to install Git. Note it is recommended that you close Visual Studio Code before installing Git, then
reopen Visual Studio Code after Git is installed.
-
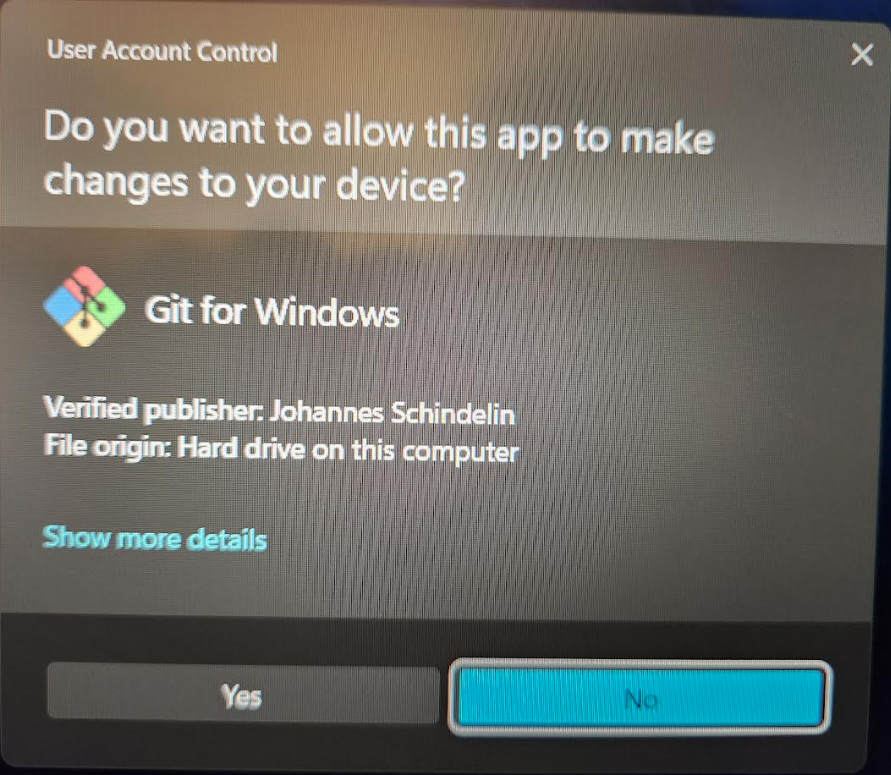
Step 6: You may be prompted by Windows to allow the file to be run. Click "Yes."
-
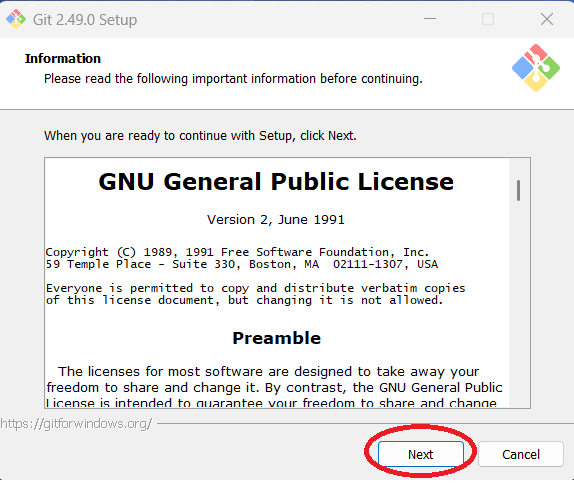
Step 7: Click "Next" to accept the GNU General Public License.
-
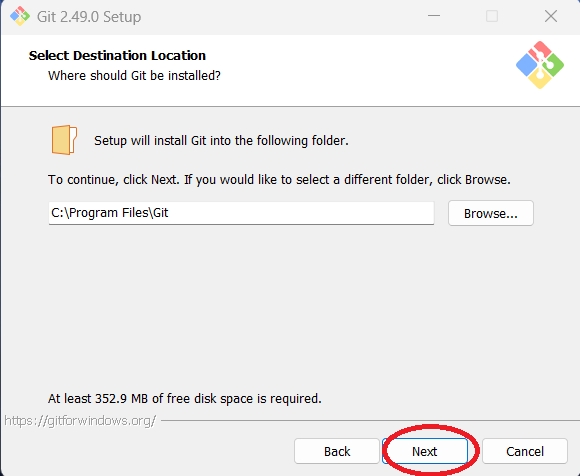
Step 8: You can change the directory where Git will be installed or leave the default. The author
used the default. Click "Next."
-
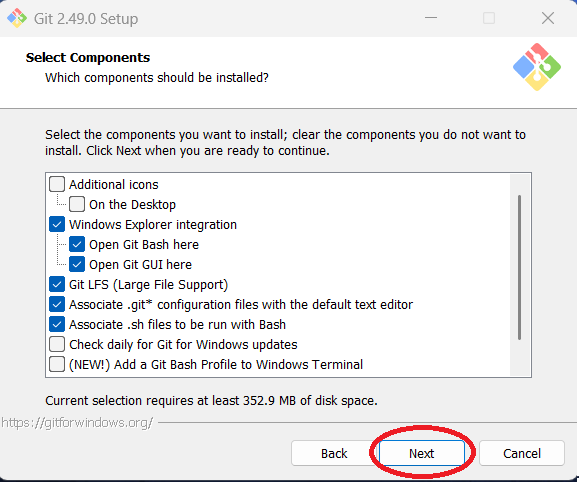
Step 9: You can add or remove components and click "Next" when done. The author left the defaults,
with the exception of unchecking the Scalar add-on (used to manage large repositories). Note that you may
need to use the scroll bar to see all the options and modify your selection.
-
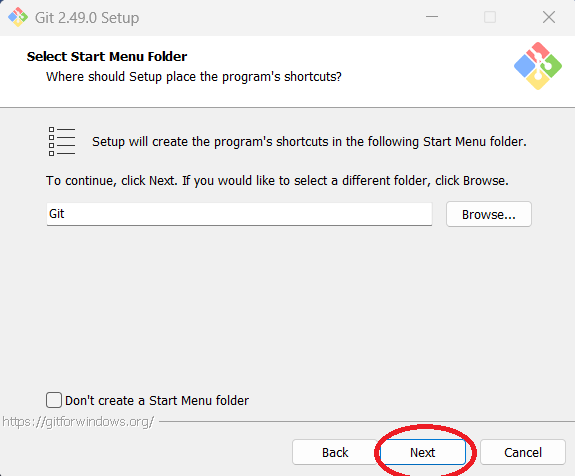
Step 10: You can change the start menu folder or stay with the default configuration. The author used
the default. Click "Next."
-
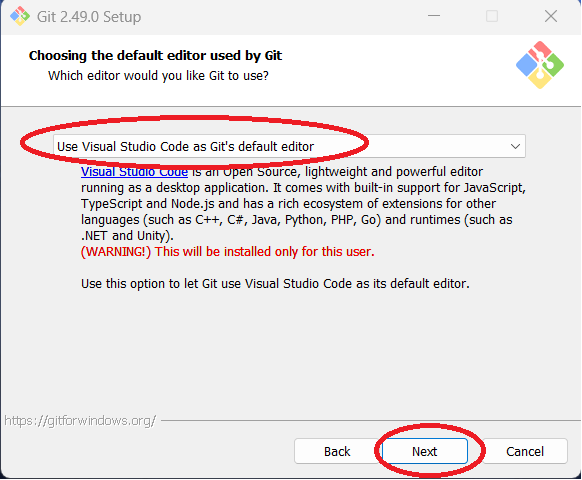
Step 11: You will be prompted to choose a default editor for Git. While you can use VIM (the default
option in the dropdown menu) as Git's editor, the author has chosen to use Visual Studio Code. Click "Next"
when you are ready. Note that if you install Git first and then install Visual Studio Code afterwards,
you may not see this option.
-
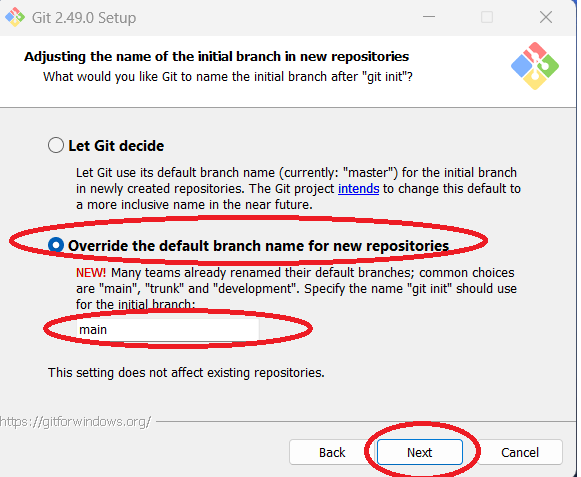
Step 12: Depending on the needs of your team and your organization, you may need to "Let Git decide"
the initial branch name for new repositories, or you may need to override the default branch name and use a
specific name. The author has chosen the "Override" option with the name "main." Click "Next" when done.
-
Step 13: If you want, you can adjust your PATH environment. The author chose the default (which is
the "Recommended" option.) Click "Next."
-
Step 14: You can adjust the SSH executable. The author used to default. Click "Next."
-
Step 15: You can adjust the HTTPS transport backend settings. Note this screen may be different if
you are not using Windows. The author used the defaults. Click "Next."
-
Step 16: You can adjust how to configure line ending conversions. The author chose the defaults.
Click "Next."
-
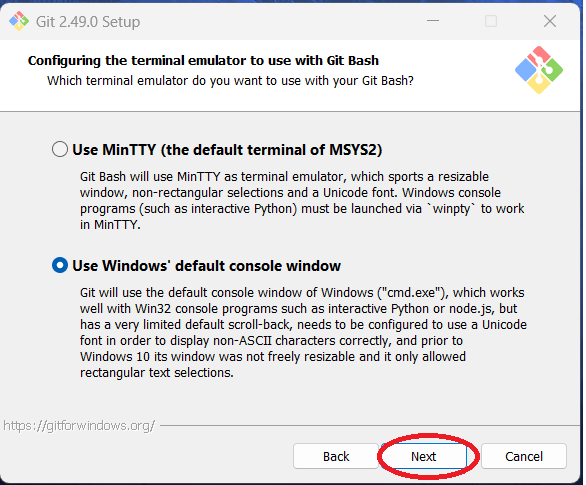
Step 17: You can configure the terminal editor used for Git Bash. The author chose to use the
Window's default console. Note the author is using Windows 11 and will be coding solutions using Python.
Click "Next."
-
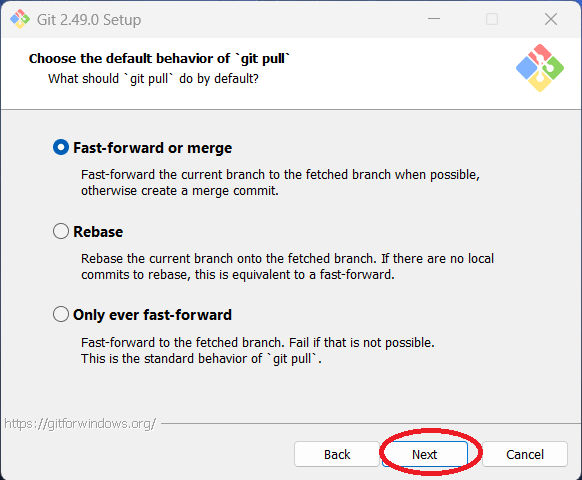
Step 18: You can choose the default "git pull" behavior. The author used the default (Fast-forward or
merge). Click "Next."
-
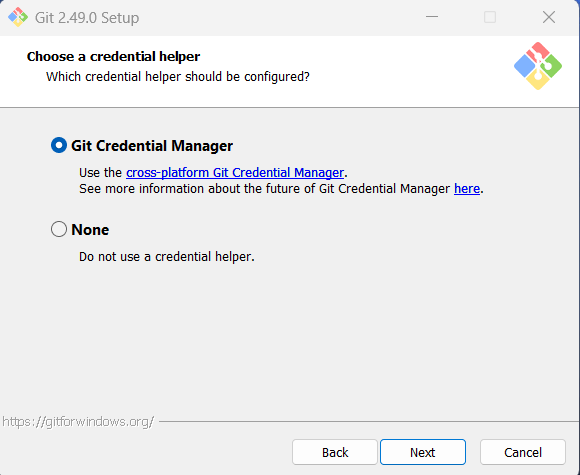
Step 19: You can choose to use Git Credential Manager or not. The author chose to use it. Click
"Next."
-
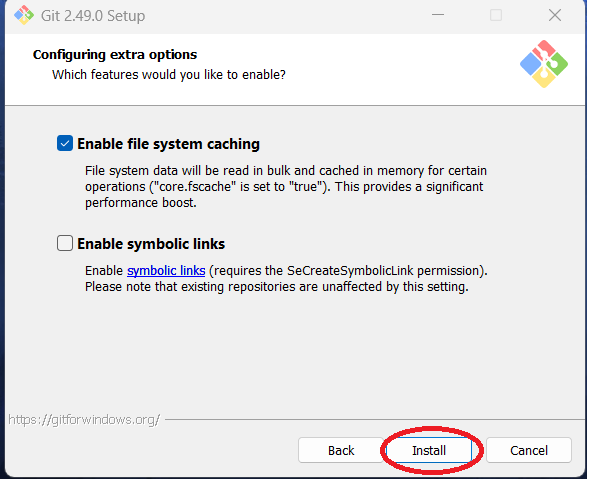
Step 20: You can enable extra options. The author chose the defaults, which is to enable file system
caching but not symbolic links. Click "Install."
-
Step 21: You should see a status bar screen showing the installation progress.
-
Step 22: Once done, you can choose to view the release notes and/or launch Git Bash. The author chose
neither option. Click "Finish."
-
Step 23: With Git installed, you should now restart your laptop. Once done, restart Visual Studio
Code and move to the next guide (Step By Step — Connect Visual
Studio Code to GitHub) where you will learn how to clone the repository you created in GitHub to
your local machine using Git and how to use Visual Studio code to push changes back to GitHub.